受精后不同时间静水压力冲击诱导溪鳟鱼三倍体血细胞的形态特征
Abstract
This study showed differences in the occurrence of blood cell alteration in triploid brook trout. The triploidisation was induced by hydrostatic shock pressure at 9500 psi for 5 min at different times after fertilisation (22.5, 27.5, 32.5, 37.5, 42.5, 47, 5, 52.5 and 62.5 min). The pressure shocks at 32.5 and 37.5 min after fertilisation caused the lowest share of pathologically altered blood cells in triploid fish.
这项研究表明,三倍体溪鳟鱼血细胞改变的发生存在差异。受精后不同时间(22.5、27.5、32.5、37.5、42.5、47、5、52.5和62.5 min)在9500 psi下静水冲击压力5 min诱导三倍化。受精后 32.5 分钟和 37.5 分钟的压力冲击导致三倍体鱼中病理改变的血细胞比例最低。
关键字:
鱼 基因组作 Salvelinus fontinalis 红细胞 白细胞
Introduction
Triploidisation is a widely used method for producing sterile fish populations. The most effective method of production of triploid fish is application of pressure shocks (Pandian and Koteeswaran 1998). However triploid red tilapia was produced both by heat shocks and cold shocks (Pradeep, Srijaya, Bahuleyan et al. 2012; Pradeep, Srijaya, Papini et al. 2012). Selection of appropriate technical parameters for the experimental treatment of different fish species is not easy, and requires a lot of experience and skills to check the final result, for example ploidy verification in experimental groups of fish using cytogenetic or cytometric methods (Benfey et al. 1984; Johnstone and Lincoln 1986). In the red tilapia, identification of triploid individuals was conducted based on nuclear volume, cytoplasmic volume and nucleus surface area of erythrocytes (Pradeep et al. 2011). The most suitable method for ploidy verification in brook trout, Salvelinus fontinalis, seems to be an erythrocyte dimensions study from blood smears (Woznicki and Kuzminski 2002).
In triploid fish, produced by pressure or thermal shock, the alterations in erythrocytes, haemoglobin and red cell indices were observed (Benfey and Sutterlin 1984b; Benfey et al. 1984; Benfey 1999; Strunjak-Perovic et al. 2003; Wlasow et al. 2004; Dorafshan et al. 2008; Wang et al. 2010; Wlasow and Fopp-Bayat 2011). Triploidisation also influenced the changes in white blood cells, immunological defence reactions and stress response (Svobodová et al. 1998, 2001 Benfey and Biron 2000; Beyea et al. 2005; Maxime 2008; Fraser et al. 2012).
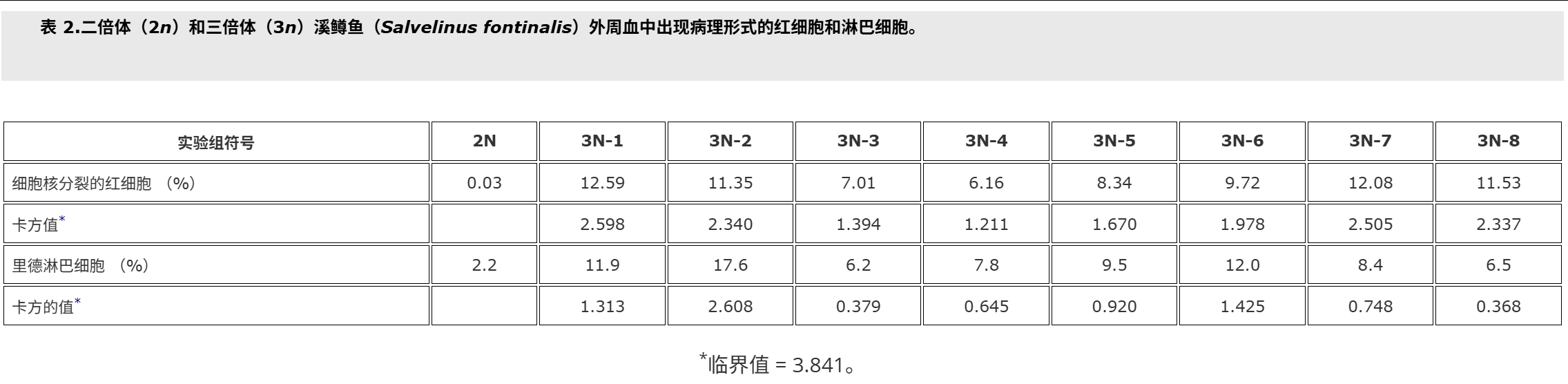
In the peripheral blood of triploid brook trout the percentage of red blood cells with divided nuclei were statistically significantly higher compared with the control group (19.1% versus 0.3%) (Wlasow et al. 2004). However, in this study the effect of triploidisation caused by shocks applied at 20 minutes after fertilisation was shown, but the influence of other technical parameters was not examined. Therefore the first purpose of the present study was to investigate the effect of differential time from fertilisation to pressure shock on the blood cell alteration in triploid brook trout. The second aim of the study was to estimate the minimal number of erythrocytes necessary for determination of percentage of red cells with divided nuclei in peripheral blood of brook trout triploids.
三倍化是一种广泛使用的生产不育鱼种群的方法。生产三倍体鱼最有效的方法是施加压力冲击(Pandian 和 Koteeswaran1998).然而,三倍体红罗非鱼是由热冲击和冷冲击产生的(Pradeep、Srijaya、Bahuleyan 等人。2012;普拉迪普、斯里贾亚、帕皮尼等人。2012).为不同鱼类的实验处理选择合适的技术参数并不容易,需要大量的经验和技能来检查最终结果,例如使用细胞遗传学或细胞术方法对鱼类实验组进行倍性验证(Benfey 等人。1984;约翰斯通和林肯1986).在红罗非鱼中,根据红细胞的核体积、细胞质体积和细胞核表面积进行三倍体个体的鉴定(Pradeep 等人。2011).最合适的溪鳟鱼倍性验证方法,Salvelinus fontinalis,似乎是通过血涂片进行红细胞尺寸研究(Woznicki 和 Kuzminski2002).
在由压力或热冲击产生的三倍体鱼中,观察到红细胞、血红蛋白和红细胞指数的改变(Benfey 和 Sutterlin1984年b;本菲等人。1984;本菲1999;Strunjak-Perovic 等人。2003;Wlasow 等人。2004;多拉夫山等人。2008;王等人。2010;Wlasow 和 Fopp-Bayat2011).三倍化还影响白细胞、免疫防御反应和应激反应的变化(Svobodová 等人。1998,2001本菲和比隆2000;贝亚等人。2005;马克西姆2008;弗雷泽等人。2012).
在三倍体溪鳟鱼的外周血中,与对照组相比,细胞核分裂的红细胞百分比在统计学上显着更高(19.1% 对 0.3%)(Wlasow 等人。2004).然而,在这项研究中,显示了受精后 20 分钟施加的冲击引起的三倍化的影响,但没有检查其他技术参数的影响。因此,本研究的首要目的是研究从受精到压力休克的时间差异对三倍体溪鳟鱼血细胞改变的影响。该研究的第二个目的是估计测定溪鳟鱼三倍体外周血中细胞核分裂的红细胞百分比所需的最小红细胞数量。
材料和方法
Material and methods
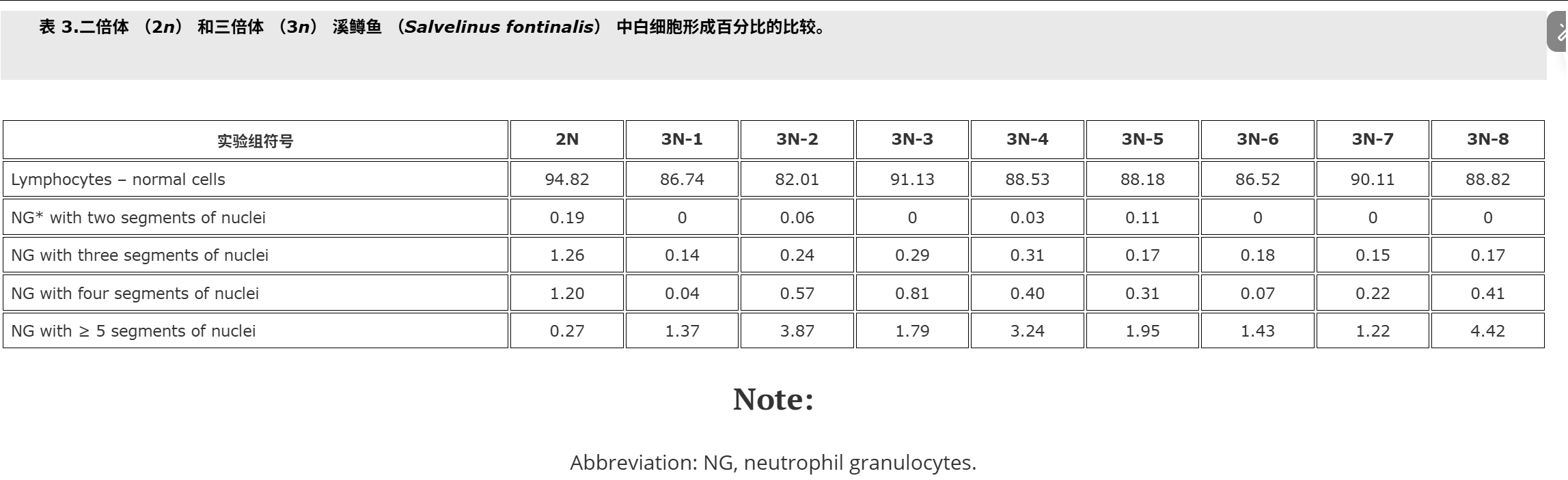
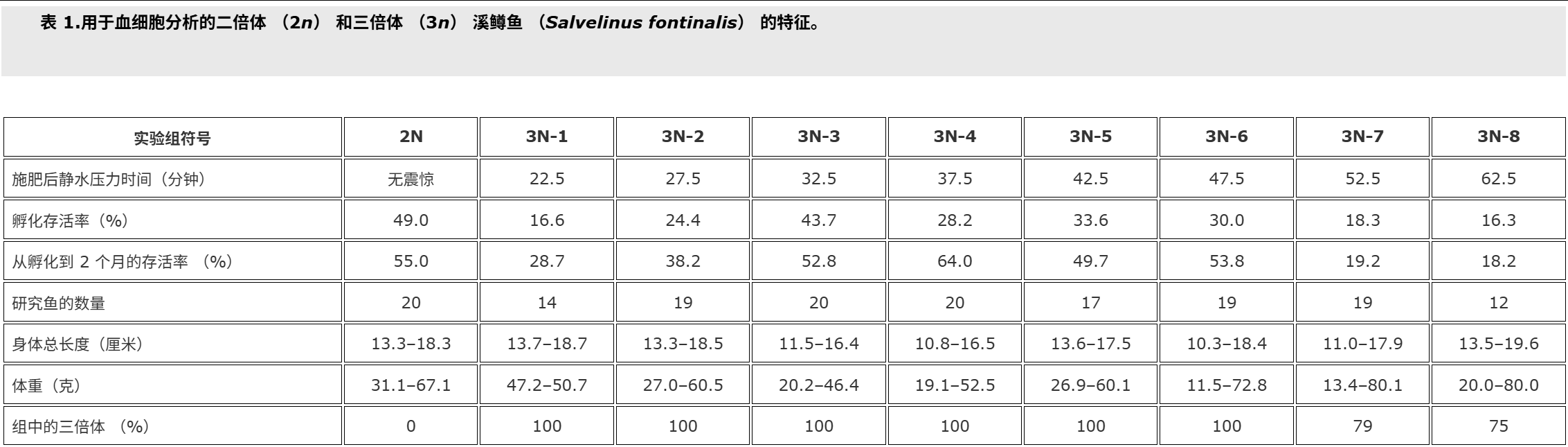
Fish used for this study were cultured at the Salmonid Research Department in Rutki (Institute of Inland Fisheries in Olsztyn, Poland). Both diploids (2n) and triploids (3n) came from the same lot of eggs. Triploid brook trout Salvelinus fontinalis (Mitchill) were obtained by using hydrostatic pressure shock of 9500 psi (65.5 × 103 kPa) on eggs at 10°C (Deeley and Benfey 1995). The pressure shock duration was 5 minutes, but time from fertilisation to shock varied in the experimental groups, and ranged from 22.5 min (group 3N-1) to 62.5 min. (group 3N-8, Table ).The diploid (control – 2N, 3N) received no pressure shock. Fish of the experimental groups were kept in separate tanks supplied with river water. During the experiment prophylactic chloramine baths were used twice a week. These baths are carried out during each rearing of fish at the Salmonid Research Department in Rutki (Institute of Inland Fisheries in Olsztyn, Poland) due to the presence of pathogens in the water supply hatchery and rearing system. Fish were fed granulate feed BioMar (Denmark). Survival from hatching to the collection of blood is shown in Table . Two months after hatching blood was collected from the caudal vessels to heparinised syringes. Propiscin (0.2% etomidate, Inland Fisheries Institute in Olsztyn, Poland) was used as an anaesthetic (0.5 ml l−1 of water for 10 min) in all experimental groups. Fish expected to be triploids (eight experimental groups, Table ) and diploids (20 specimens) were used for preparing blood smears. Smears were fixed in 95% methanol for 3 minutes, left to air dry and stained with 20% Giemsa solution for 15 minutes. The percentage of erythrocytes with divided nuclei was determined based on the observation of 300 cells from two slides for fish. For the study of white blood cells 200 cells were analysed, and the following forms have been studied: normal lymphocytes, Rieder’s lymphocytes (cells with divided nuclei), and neutrophil granulocytes (NGs) with 2, 3, 4 and ≥ 5 segments of nuclei. The identification was based on the leukocyte descriptions published by Lehmann and Stürenberg (1975).
用于本研究的鱼是在鲁特基的鲑鱼研究部(波兰奥尔什丁内陆渔业研究所)养殖的。二倍体 (2n) 和三倍体 (3n) 都来自同一批卵。三倍体溪鳟鱼 Salvelinus fontinalis (Mitchill) 是通过在 10°C 下对鸡蛋进行 9500 psi (65.5 × 103 kPa) 的(上海瑾瑜出售)静水压力机冲击获得的 (Deeley 和 Benfey)1995).压力休克持续时间为5 min,但实验组从受精到休克的时间各不相同,从22.5 min(3N-1组)到62.5 min不等(3N-8组,表).二倍体(对照 – 2N、3N)没有受到压力冲击。实验组的鱼被饲养在单独的水箱中,供水。在实验期间,每周使用两次预防性氯胺浴。由于供水孵化场和饲养系统中存在病原体,这些浴是在 Rutki 的鲑鱼研究部(波兰奥尔什丁内陆渔业研究所)每次养鱼期间进行的。鱼被喂食颗粒饲料 BioMar(丹麦)。从孵化到采血的存活率见表.孵化后两个月,从尾部血管收集血液到肝素注射器中。使用普罗匹辛(0.2% 依托咪酯,波兰奥尔什丁内陆渔业研究所)作为麻醉剂(0.5 毫升升−1水 10 分钟)在所有实验组中。预计为三倍体的鱼(八个实验组,表)和二倍体(20个标本)用于制备血涂片。将涂片固定在95%甲醇中3分钟,风干并用20%吉姆萨溶液染色15分钟。根据对两张鱼类载玻片的 300 个细胞的观察,确定具有分裂细胞核的红细胞百分比。为了研究白细胞,分析了 200 个细胞,并研究了以下形式:正常淋巴细胞、里德淋巴细胞(细胞核分裂的细胞)和具有 2、3、4 和 ≥ 5 段细胞核的中性粒细胞 (NG)。鉴定基于 Lehmann 和 Stürenberg 发表的白细胞描述(1975).
Simultaneously chromosome preparations (10 specimens from each experimental group) and the erythrocyte nuclei major axis measurements (all fish from each treatment) were done using procedure described by Woznicki and Kuzminski (2002) in order to confirm fish ploidy. Differential cell counts were made under a 1000 × magnification.
Statistical analyses were performed on data from microscopic observations as the actual number of segmented nuclei in analysed preparations. In Tables and data were summarised in the form of percentages. All statistical analyses were evaluated at a significance level of 0.05. The chi-square test was used to evaluate the differences in proportion of “abnormal” to normal erythrocytes and leukocytes in triploid and diploid trout. Statistical differences between the observed number of red blood cells with segmented nucleus in the groups of 2N and 3N fish were calculated based on an alternative non-parametric analysis of variance – ANOVA Kruskal–Wallis (α = 0.05). In order to investigate how many nuclei should be counted to show the dependence of the number of nuclei divided by ploidy the Friedman ANOVA test was used. Data were collected from 71 fish, step by step as follows: 50 nuclei were observed and selected as normal and divided, and then the next 50 nuclei were observed and also selected as normal and divided (two or more parts), after that the cyclic analysis of next 50 nuclei was conducted. A total of 300 nuclei were counted. It was hypothesised that the results obtained for the count of 50, 100, 150, 200, 250 and 300 nuclei did not differ significantly and therefore the study of ploidy is sufficient to perform only counts of 50 nuclei.
同时使用 Woznicki 和 Kuzminski 描述的程序进行染色体制备(每个实验组 10 个标本)和红细胞核长轴测量(来自每个处理的所有鱼)(2002)以确认鱼的倍性。在 1000 ×放大倍率下进行差异细胞计数。
对来自显微观察的数据进行统计分析,作为分析制剂中分段细胞核的实际数量。在表格中和数据以百分比的形式汇总。所有统计分析均以 0.05 的显着性水平进行评估。采用卡方检验评估三倍体和二倍体鳟鱼中“异常”与正常红细胞和白细胞比例的差异。根据替代非参数方差分析 - 方差分析 Kruskal-Wallis (α = 0.05) 计算 2N 和 3N 鱼组中观察到的具有分段细胞核的红细胞数量之间的统计差异。为了研究应该计算多少个细胞核以显示细胞核数除以倍性的依赖性,使用了弗里德曼方差分析检验。从71条鱼中收集数据,逐步如下:观察50个细胞核,选择正常并分裂,然后观察接下来的50个细胞核,也选择为正常并分裂(两个或多个部分),然后对接下来的50个细胞核进行循环分析。总共计算了 300 个细胞核。据推测,对 50、100、150、200、250 和 300 个细胞核的计数获得的结果没有显着差异,因此倍性研究足以仅对 50 个细胞核进行计数。